Introduction of Gwangyang
GWANGYANG
Introduction of Gwangyang
Environment
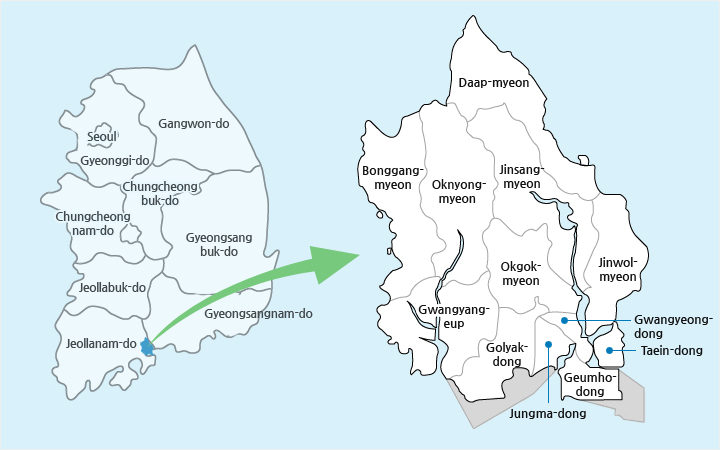
Location of Gwangyang
Located in the middle of the southernmost part of the Korean Peninsula, Gwangyang is a strategic city in national maritime administration. It borders Gurye to the north, Hadong to the east, Suncheon to the west, and the Gwangyang Bay to the south. Overlooking the Yeosu, Gwangyang is in the heart of the Gwangyang Bay and Jinju area. Being a strategic location, the city has served as the gateway for cultural exchanges between the Yeongnam and Honam areas and plays an important part in balanced national development.
| Types | East End | West End | South End | North End |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Osa-ri, Jinwol-myeon | Sinnyong-ri, Bonggang-myeon | Jijin-do, Geumho-dong | Hacheon-ri, Daap-myeon |
| Longitude and Latitude | East Longitude 127°47′ | East Longitude 127°32′ | North Latitude 34°53′ | North Latitude 35°11′ |
Access
The Honam Expressway and Namhae Expressway, connecting Gwangju and Busan, cross the southern part of Gwangyang including Gwangyang-eup, Bonggang-myeon, Jungma-dong, Okgok-myeon, and Jinwol-myeon. From the sea, the city is on the route toward North America as well as Europe. Thirty minutes by car from the city are Yeosu Airport and Sacheon Airport. As such, Gwangyang boasts superb transportation access from the sea, air, and land.
| Types | Transportation Network |
|---|---|
| Road |
|
| Railway |
|
| Airport |
|
| Hinterland Transportation |
|
Climate
Jirisan Mountain and Baegunsan Mountain protect Gwangyang from northwesterly seasonal winds. Influenced by oceanic climate due to warm current from the southern sea, Gwangyang receives the largest amount of sunlight in Korea, leading to the production of high quality farm products. Lacking days with strong wind, Gwangyang is surrounded by a stable temperature, which offers an ideal environment for the development of its outstanding port.
Temperature
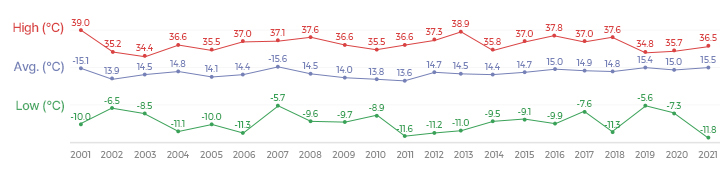
| Types | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Highest Temperature | 34.0 | 39.0 | 35.2 | 34.4 | 36.6 | 35.5 | 37.0 | 37.1 | 37.6 | 36.6 | 35.5 | 36.6 | 37.3 | 38.9 | 36.7 | 37.0 |
| Average Temperature | 14.4 | 15.1 | 13.9 | 14.4 | 14.8 | 14.1 | 14.4 | 15.6 | 14.5 | 14.0 | 13.8 | 13.6 | 14.7 | 14.5 | 14.9 | 14.7 |
| Lowest Temperature | -9.0 | -10.0 | -6.5 | -8.5 | -11.1 | -10.0 | -11.3 | -5.7 | -9.6 | -9.7 | -8.9 | -11.6 | -11.2 | -11.0 | -6.5 | -9.1 |
Temperature Change
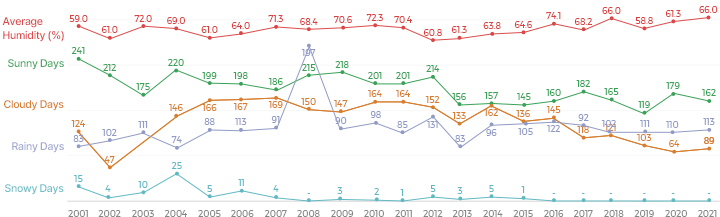
| Types | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Humidity | 59 | 59 | 61 | 72 | 69 | 61 | 64 | 71.3 | 68.4 | 70.6 | 72.3 | 70.4 | 60.8 | 61.3 | 63.8 | 64.6 |
| Number of Clear Days | 185 | 241 | 212 | 175 | 220 | 199 | 198 | 196 | 215 | 218 | 201 | 201 | 214 | 156 | 157 | 145 |
| Number of Cloudy Days | 65 | 124 | 47 | 72 | 146 | 166 | 167 | 169 | 150 | 147 | 164 | 164 | 152 | 133 | 162 | 136 |
| Number of Rainy Days | 100 | 83 | 102 | 111 | 74 | 88 | 113 | 91 | 197 | 90 | 98 | 85 | 131 | 83 | 96 | 105 |
| Number of Snowy Days | 11 | 15 | 4 | 10 | 25 | 5 | 11 | 4 | - | 3 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 1 |
Rainfall (㎜)
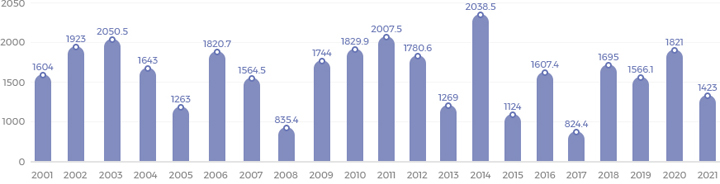
| Types | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall | 1,833 | 1,604 | 1,923 | 2,050.5 | 1,643 | 1,263 | 1820.7 | 1,564.5 | 835.4 | 1,744 | 1,829.9 | 2,007.5 | 1,780.6 | 1,269.0 | 2,038.5 | 1,124.0 |